Class hierarchy of user-facing classes
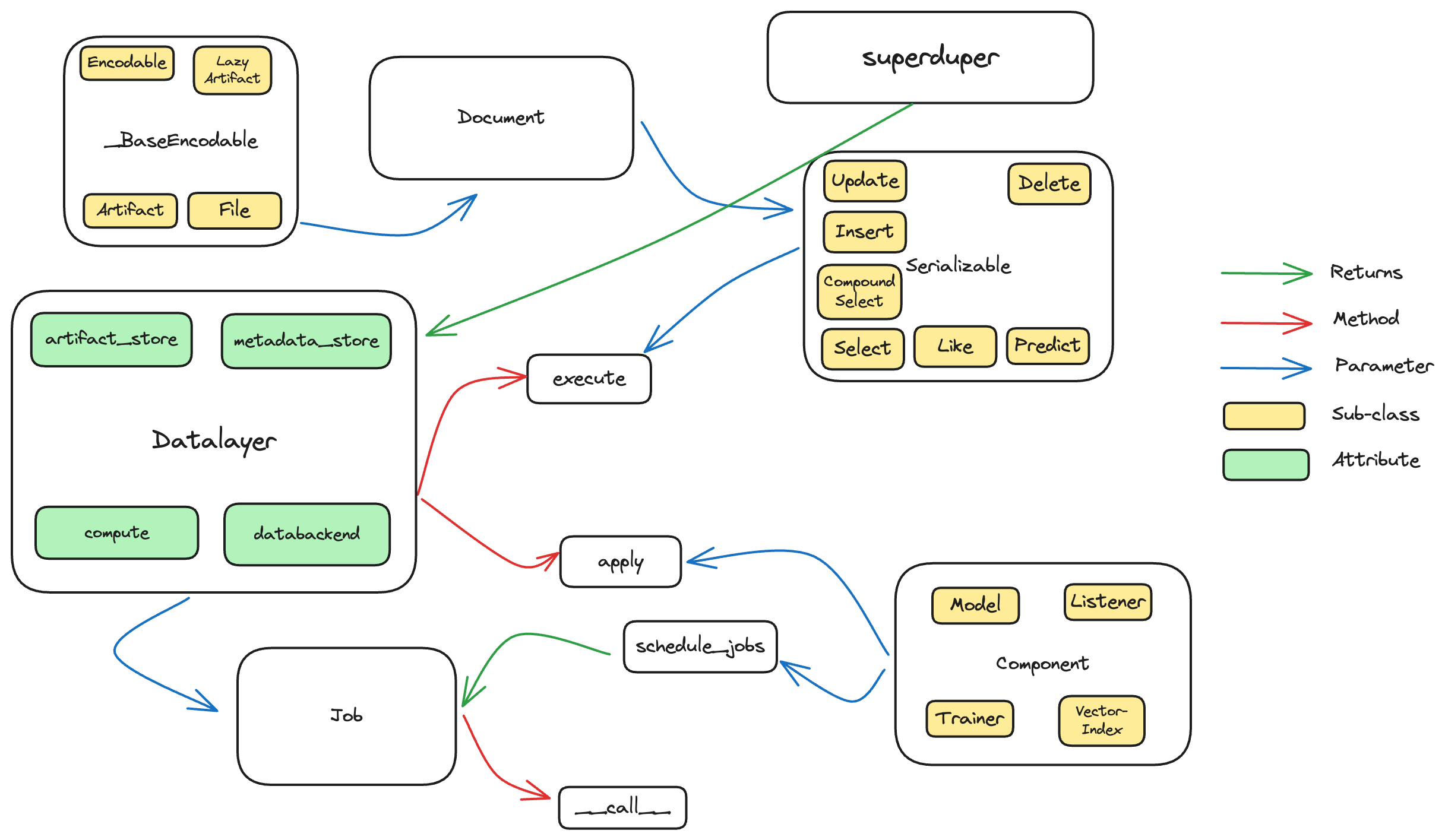
superduper
superduper is the entry point to connect and
be able to use key functionality. It returns a built Datalayer.
Datalayer
The Datalayer class, an instance of which we refer to throughout this
documentation as db, is the key entrypoint via which developers
may connect to their data-infrastructure and additional connect
AI functionality to their data-infrastructure:
The Datalayer connects to data, with the superduper function.
.apply
AI Component instances may be applied to the built Datalayer with .apply.
.execute
The data and AI outputs are accessible with queries and AI models
using the .execute method. This can include standard database queries,
vector-search queries (which include model inference) and pure model computations.
See here.
Component
AI functionality is packaged as a Component. Key implementations
are Model, Listener and VectorIndex.
Document
Document is a wrapper around standard Python dict instances,
but which can encode their contained fields as a mixture of JSON
and pure bytes. This mechanism can in principle handle any information
which Python can handle.
Since most databases can handle this type of information, this makes
Document a crucial piece in connecting AI (which operates over a range of information)
and the database.
_BaseEncodable
This is the base class, which allows superduper to decide how to save "special" data.
Serializable
An extension of Python dataclasses, but easier to get the original class back
from the serialized dictionary form. This is the base class underlying
all superduper queries and predictions as well as mixing into Component.
Job
Component instances applied with Datalayer.apply create compute-jobs
in response to incoming data, and on initialization via the Job class.
The interface on Component is Component.schedule_jobs.